[av_layerslider id=’3′]
[av_one_full first min_height=” vertical_alignment=’av-align-top’ space=’no_margin’ margin=’0px’ margin_sync=’true’ padding=’0px’ padding_sync=’true’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ radius_sync=’true’ background_color=” src=” attachment=” attachment_size=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_heading tag=’h1′ padding=’10’ heading=’Electric Bike & Electric Scooter Laws & Regulations in Canada’ color=” style=’blockquote modern-quote modern-centered’ custom_font=” size=” subheading_active=” subheading_size=’15’ custom_class=” admin_preview_bg=” av-desktop-hide=” av-medium-hide=” av-small-hide=” av-mini-hide=” av-medium-font-size-title=” av-small-font-size-title=” av-mini-font-size-title=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=”][/av_heading]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
Owning an Electric Bike in Canada is easy. These vehicles are also known as power-assisted bicycles, electric scooters, e-bikes, and e-scooters, and the laws for them are very similar to a traditional bicycle. They require no license, plates, or insurance to own or operate. In Canada, Power Assisted Bicycles are classified under Federal law, and each province can make minor changes such as age requirements. Also, each municipality can make changes as to where they are permitted to be used.
We have put together a list below to some useful links to Federal, Provincial, and municipal government websites. Power Assisted Bicycles (electric bikes, electric scooters, e-bikes, and e-scooters) are encouraged by all levels of Government in Canada.
[/av_textblock]
[av_heading tag=’h2′ padding=’10’ heading=’Overview of Electric Bike Laws in Canada’ color=” style=” custom_font=” size=” subheading_active=” subheading_size=’15’ custom_class=” admin_preview_bg=” av-desktop-hide=” av-medium-hide=” av-small-hide=” av-mini-hide=” av-medium-font-size-title=” av-small-font-size-title=” av-mini-font-size-title=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=”][/av_heading]
[/av_one_full]
[av_one_third first min_height=” vertical_alignment=’av-align-top’ space=” margin=’0px’ margin_sync=’true’ padding=’0px’ padding_sync=’true’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ radius_sync=’true’ background_color=” src=” attachment=” attachment_size=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_image src=’https://epiccycles.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/overview1-300×229.png’ attachment=’12406′ attachment_size=’medium’ align=’center’ styling=” hover=” link=” target=” caption=” font_size=” appearance=” overlay_opacity=’0.4′ overlay_color=’#000000′ overlay_text_color=’#ffffff’ animation=’no-animation’ admin_preview_bg=”][/av_image]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
Electric bikes are accepted for use in eight provinces in Canada. These provinces include Alberta, Manitoba, British Columbia, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec, Ontario, and Saskatchewan. However, there are a number of regulations that are peculiar to all eight provinces. In Canada, Electric bikes are generally limited to an output of 500 W. Additionally; they are not allowed to travel at speeds higher than 32km/h.
[/av_textblock]
[/av_one_third]
[av_one_third min_height=” vertical_alignment=” space=” custom_margin=” margin=’0px’ padding=’0px’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ background_color=” src=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_image src=’https://epiccycles.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/overview2-300×229.png’ attachment=’12407′ attachment_size=’medium’ align=’center’ styling=” hover=” link=” target=” caption=” font_size=” appearance=” overlay_opacity=’0.4′ overlay_color=’#000000′ overlay_text_color=’#ffffff’ animation=’no-animation’ admin_preview_bg=”][/av_image]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
Restrictions in the ages of drivers differ from province to province. Also, while some regions do not require a license to ride an e-bike, others require one. Another factor that is common to all provinces that allow the use of e-bikes in Canada is that every driver must wear an approved helmet to prevent accidents.
[/av_textblock]
[/av_one_third]
[av_one_third min_height=” vertical_alignment=” space=” custom_margin=” margin=’0px’ padding=’0px’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ background_color=” src=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_image src=’https://epiccycles.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/overview3-1-300×229.png’ attachment=’12411′ attachment_size=’medium’ align=’center’ styling=” hover=” link=” target=” caption=” font_size=” appearance=” overlay_opacity=’0.4′ overlay_color=’#000000′ overlay_text_color=’#ffffff’ animation=’no-animation’ admin_preview_bg=”][/av_image]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
It is easy to procure an electric bike in Canada. Bicycles that are deemed to be power assisted can be exported and imported without any severe restrictions like those placed on cars and other vehicles. Although they are accepted for use in several provinces, their usage is still somewhat restricted. Depending on the province, electric bikes are not allowed on specific roads, paths, lanes as well as thoroughfares. This restriction is not due to a federal ruling. It usually depends on the stance of the local municipality towards e-bikes.
[/av_textblock]
[/av_one_third]
[av_hr class=’invisible’ height=’50’ shadow=’no-shadow’ position=’center’ custom_border=’av-border-thin’ custom_width=’50px’ custom_border_color=” custom_margin_top=’30px’ custom_margin_bottom=’30px’ icon_select=’yes’ custom_icon_color=” icon=’ue808′ font=’entypo-fontello’ admin_preview_bg=”]
[av_codeblock wrapper_element=” wrapper_element_attributes=”]
[/av_codeblock]
[av_one_full first min_height=” vertical_alignment=” space=” custom_margin=” margin=’0px’ padding=’0px’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ background_color=” src=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_heading heading=’Province of Ontario – Frequently Asked Questions: Electric scooters, electric bicycles & e-bikes’ tag=’h2′ style=” size=” subheading_active=” subheading_size=’15’ padding=’10’ color=” custom_font=” av-medium-font-size-title=” av-small-font-size-title=” av-mini-font-size-title=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”][/av_heading]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
The province of Ontario allows for the use of electric bikes. However, there are still a few questions that need to be answered concerning the legal ways to use them. They include:
[/av_textblock]
[/av_one_full]
[av_toggle_container initial=’0′ mode=’accordion’ sort=” styling=” colors=” font_color=” background_color=” border_color=”]
[av_toggle title=’What are the safety and weight requirements for an e-bike in Ontario?’ tags=”]
To better safeguard riders, e-bikes have a weight limit of 120kg. Additionally, riders have to be at least 16 years old with all passengers wearing approved helmets. Finally, modifications that allow an e-bike to exceed speeds of 32km/h are not allowed.
[/av_toggle]
[av_toggle title=’Can I remove my electric bike’s pedals?’ tags=”]
No. An electric bike without pedals is no longer accepted as an electric bike according to the Highway Traffic Act. This makes your bike illegal. You could be issued a ticket for using it on government property.
[/av_toggle]
[av_toggle title=’Can I use my e-bike if it weighs over 120kg?’ tags=”]
Yes, you can still use your electric bike. However, it will no longer be considered an electric bike by law. You would have to obtain moped licensing, insurance, and registration requirements.
[/av_toggle]
[av_toggle title=’Can I ride an electric bike with a suspended license?’ tags=”]
This depends on the reasons behind the suspension of your license. If your driver’s license is suspended due to a conviction that led to a driving prohibition, you can not ride an electric bike. However, if the circumstances behind your license been suspended are different, you can discuss with a licensed lawyer to examine your options.
[/av_toggle]
[/av_toggle_container]
[av_hr class=’invisible’ height=’50’ shadow=’no-shadow’ position=’center’ custom_border=’av-border-thin’ custom_width=’50px’ custom_border_color=” custom_margin_top=’30px’ custom_margin_bottom=’30px’ icon_select=’yes’ custom_icon_color=” icon=’ue808′ font=’entypo-fontello’ admin_preview_bg=”]
[av_one_full first min_height=” vertical_alignment=” space=” custom_margin=” margin=’0px’ padding=’0px’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ background_color=” src=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_heading tag=’h2′ padding=’10’ heading=’Ontario Ministry of Transportation – Legalities of electric bicycles, electric scooters & e-bikes’ color=” style=” custom_font=” size=” subheading_active=” subheading_size=’15’ custom_class=” admin_preview_bg=” av-desktop-hide=” av-medium-hide=” av-small-hide=” av-mini-hide=” av-medium-font-size-title=” av-small-font-size-title=” av-mini-font-size-title=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=”][/av_heading]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
Electric bikes are electricity powered bicycles that are made to look like conventional scooters or bicycles. However, there are many schools of thought as to what an electric bike constitutes. In Ontario, the legalities and the make-up of an electric bike are clearly defined.
[/av_textblock]
[/av_one_full]
[av_toggle_container initial=’0′ mode=’accordion’ sort=” styling=” colors=” font_color=” background_color=” border_color=”]
[av_toggle title=’In Ontario, a motorized bike is only considered to be an electric bike if it has:’ tags=”]
- Working pedals
- Steering handlebars
- A power output that is less than or equal to 500 Watts
- Maximum speed levels of 32km/h
- A weight of 120kg or less
- A label designed by the manufacturer, stating that your electric bike conforms to federal definitions for a motorized bicycle
[/av_toggle]
[av_toggle title=’Additionally for riders:’ tags=”]
- You have to be 16 years or older
- You always have to wear an approved helmet
- You also have to obey the same road rules as other cyclists
[/av_toggle]
[av_toggle title=’Other essential legalities that you need to contend with include the fact that you can’t ride an electric bike:’ tags=”]
- On specific highways controlled by provincial authorities. Some of these highways include the Queensway, the Kitchener-Waterloo Expressway, and the Queen Elizabeth way.
- On municipal sidewalks, roads, and paths where the use of bicycles is already banned by civil law.
- On public sidewalks, roads, bike trails, and bike paths where the use of electric bikes has been prohibited.
[/av_toggle]
[/av_toggle_container]
[av_textblock size=” font_color=” color=” av-medium-font-size=” av-small-font-size=” av-mini-font-size=” admin_preview_bg=”]
For more info on frequently asked questions on electric bike usage in the province of Ontario, please visit:
Ministry of Transportation – Ontario: Frequently Asked Questions – Electric Bicycles
[/av_textblock]
[av_one_full first min_height=” vertical_alignment=” space=” custom_margin=” margin=’0px’ padding=’0px’ border=” border_color=” radius=’0px’ background_color=” src=” background_position=’top left’ background_repeat=’no-repeat’ animation=” mobile_breaking=” mobile_display=”]
[av_tab_container position=’top_tab’ boxed=’border_tabs’ initial=’1′]
[av_tab title=’Province of Ontario – Highway Traffic Act’ icon_select=’no’ icon=’ue800′ font=’entypo-fontello’]
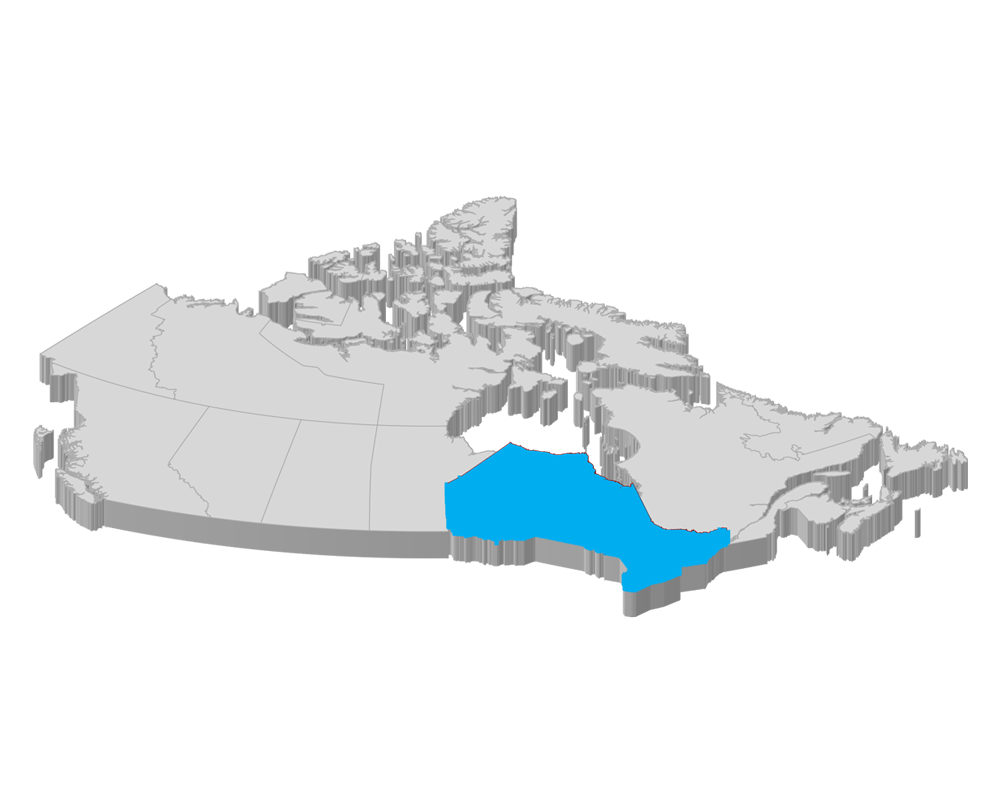 Electric bikes used to occupy the middle ground between bicycles and motor vehicles. However, in 2000, they were given their category by Canada’s prestigious Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations. Today, in Ontario, the Highway traffic act considers e-bikes to be completely different from other types of vehicles. They are separate and have their laws.
Electric bikes used to occupy the middle ground between bicycles and motor vehicles. However, in 2000, they were given their category by Canada’s prestigious Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations. Today, in Ontario, the Highway traffic act considers e-bikes to be completely different from other types of vehicles. They are separate and have their laws.
According to the Ontario Highway Traffic Act, you can ride an electric bike without a valid driver’s license. However, there is a specific speed limit you have to follow. Electric bike laws in Ontario states that electric bikes must not go over a speed of 32mph. The Highway Traffic Act also states that electric bikes that have been derestricted to increase their speed limits are considered illegal.
In terms of safety, the Ontario highway traffic act state that all electrical terminals on an e-bike must be covered. This is done to reduce the risk of dangerous accidents. Usually, new electric bikes have this protective feature built in.
On the subject of specifications, the wheels of an electric bike must not be less than 35/350mm according to the Ontario Highway Traffic Act. This is the best way to make sure that these motorized bikes can withstand the rigours of use on selected roadways. Finally, riders must be able to provide a means of identification.
For more details about riding electric bikes in Ontario, please check:
Ministry of Transportation – Ontario: FAQs – Electric Bicycles
[/av_tab]
[av_tab title=’Province of Quebec – Rules for electric bicycles, electric scooters, and e-bikes’ icon_select=’no’ icon=’ue800′ font=’entypo-fontello’]
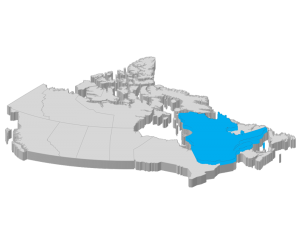 The rules for the use of an electric bike in the province of Quebec differ slightly. The rules for power ratings of less than 500 watts still stand. In Quebec, your e-bike can have up to three wheels. Although, it must be ridden while wearing a helmet in which the law states must be made entirely of a sturdy shell and a specially padded interior.
The rules for the use of an electric bike in the province of Quebec differ slightly. The rules for power ratings of less than 500 watts still stand. In Quebec, your e-bike can have up to three wheels. Although, it must be ridden while wearing a helmet in which the law states must be made entirely of a sturdy shell and a specially padded interior.
In Quebec, the law requests that all e-bikes must bear the original label imprinted by manufactures. Also, all extra accessories that are used have to comply with the Automobile Insurance Act and the Highway Safety Code. Electric bikes can be used on all roads except highways (including their exit and access ramps). You do not need to specially register an electric bike, although there are some restrictions on licensing. Riders over the age of 18 do not require any license. However, motorists between the age of 14-17 require a Class 6D license that bears authorization to operate a scooter, e-bike or moped. The minimum age for riders in Quebec is 14.
All riders have to follow regular road rules the same as other vehicle users. Additionally, the speed limit for e-bikes in Quebec is 32mph. This is one regulation that most of the provinces that allow the use of an e-bike on the municipal property has.
To get more information about the rules governing electric bike usage in Quebec, please visit:
Quebec: Road Safety on an Electric Bike
[/av_tab]
[/av_tab_container]
[av_tab_container position=’top_tab’ boxed=’border_tabs’ initial=’1′]
[av_tab title=’City of Ottawa – Ottawa City Cycling Plan’ icon_select=’no’ icon=’ue800′ font=’entypo-fontello’]
 The city of Ottawa is completely committed to integrating electric bike riders into its community. It is a city that believes in the long term health and social benefits of cycling, especially when it comes to electric bikes.
The city of Ottawa is completely committed to integrating electric bike riders into its community. It is a city that believes in the long term health and social benefits of cycling, especially when it comes to electric bikes.
In 2013, the Ottawa City Cycling Plan was thought up and implemented. The 2013 Ottawa Cycling Plan was devised as a long-term strategic plan to strengthen and improve the state of cycling in the city. The latest cycling plan is an update to a similar initiative that was thought up in 2008. This current plan was developed to build a socially conscious Ottawa, that promoted the ideals of cycling and the use of e-bikes.
The Ottawa City plan involved upgrades to the city’s transportation plan and routes, pedestrian plan and the provision of infrastructure geared at making sure that users of e-bikes and other bicycles can enjoy cycling. A complete look at the policy as well as cycling networks and maps can be found online using the GeoOttawa mapping tool.
To check more details of the Ottawa City Cycling Plan, please visit:
Ottawa City Cycling Plan
[/av_tab]
[av_tab title=’City of Montreal Police Services – Power Assisted Bicycles’ icon_select=’no’ icon=’ue800′ font=’entypo-fontello’]
 In Montreal, electric bikes are described as vehicles with a pedal system that are powered exclusively by electricity. To drive an electric bike in Montreal, you have to be over the age of 18. Alternatively, you have to hold at least a Class 6D driver’s license.
In Montreal, electric bikes are described as vehicles with a pedal system that are powered exclusively by electricity. To drive an electric bike in Montreal, you have to be over the age of 18. Alternatively, you have to hold at least a Class 6D driver’s license.
Also, electric bikes in Montreal have to be equipped with pedals, must be able to be propelled by human energy and must have a power output of less than or equal to 500W. This also means that the electric bike must have a speed limit of 32km/h on even ground. Electric bikes that have been tweaked to deliver speeds of over 32km/h are considered to be illegal.
Safety is important to the city of Montreal. That is why authorities have determined that electric bikes must have:
- An enabling mechanism that is designed to turn on the electric motor. This mechanism must be different from the e-bike accelerator and must be fitted to be easily operable by the rider.
- A safety mechanism that prevents the electric motor from working before the e-bike reaches speeds of 3km/h
Related article: How an Electric Bike Works?
For more information on power-assisted bicycle rules and regulations as determined by the city of Montreal Police Services visit:
SPVM: Power Assisted Bicycle
[/av_tab]
[av_tab title=’City of Toronto ‘ icon_select=’no’ icon=’ue800′ font=’entypo-fontello’]
 Classification of electric scooters, electric bicycles, e-bikes, moped, and motor scooters:
Classification of electric scooters, electric bicycles, e-bikes, moped, and motor scooters:
Cycling is a fast growing mode of transportation in Toronto. The City of Toronto is also doing its bit by putting up regulations to make the use of electric bikes safer and more inviting. The use of e-bikes and other bicycles have served to reduce congestion in Toronto, making the streets cleaner and promoting a healthier environment in general.
There are bike lanes in Toronto; bike parks have been installed, while maps that also display the city’s bike network have been put into distribution. In Toronto, different classifications are made to distinguish an electric bike from scooters.
In Toronto, e-bikes are referred to as pedelecs, and they are used to describe any vehicle with handlebars, working pedals, an electric motor with an output of less than 500W and a speed limit of 32km/h. They can be used on all cycling infrastructure, including cycle tracks, multi-use trails, and bike lanes.
Scooters, on the other hand, are vehicles that meet the city of Toronto’s definition of e-bikes but not of pedelecs. They are not to be driven on cycle tracks or multi-use trails.
For more details on the city of Toronto’s unique classification of electric scooters, electric bikes and mopeds, please check out this web page:
Streets, Parking & Transportation: Cycling in Toronto
[/av_tab]
[/av_tab_container]
[/av_one_full]



















